Изучаем Avalanche (AVAX)
Что такое Avalanche?
Avalanche (AVAX) — это криптовалюта и блокчейн-платформа, конкурирующая с Ethereum. AVAX — это собственный токен блокчейна Avalanche, который, как и Ethereum, использует смарт-контракты для поддержки различных блокчейн-проектов.
Блокчейн Avalanche может обеспечить почти мгновенную завершенность транзакций. AVAX используется для оплаты комиссий за обработку транзакций и защиты сети Avalanche, а также выступает в качестве базовой расчетной единицы среди блокчейнов в сети Avalanche.

* Avalanche — это блокчейн-платформа с собственной валютой AVAX.
* Avalanche — конкурент Ethereum, который отдает предпочтение масштабируемости и скорости обработки транзакций.
* AVAX используется для защиты блокчейна Avalanche и оплаты комиссий за транзакции в сети.
* Комиссии за транзакции и скорость создания монет AVAX определяются с использованием модели управления.
Сообщается, что блокчейн Avalanche может обрабатывать 4500 транзакций в секунду. Запущенный в 2020 году Avalanche стремится быть быстрым, универсальным, безопасным, недорогим и доступным. Avalanche — это проект с открытым исходным кодом , что означает, что каждый может просматривать и вносить свой вклад в код платформы.
Понимание Avalanche
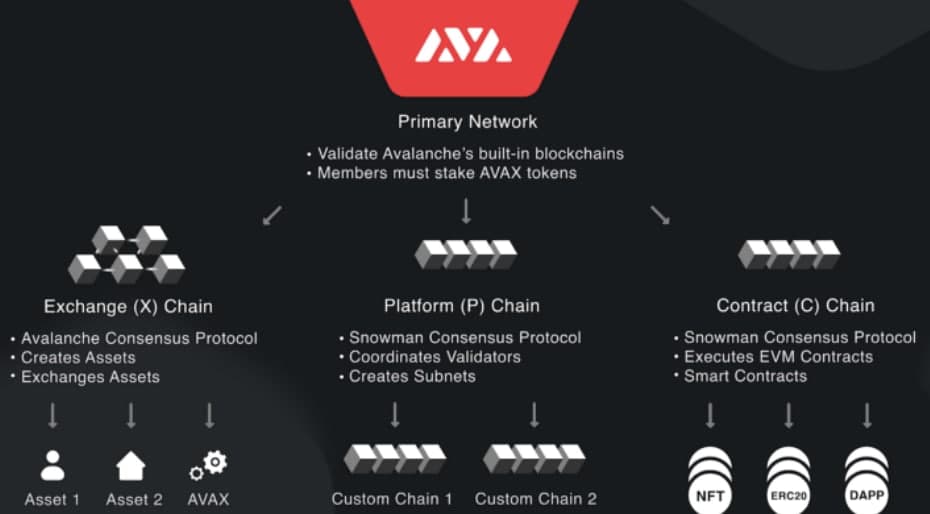
Платформа смарт-контрактов Avalanche поддерживает как децентрализованные приложения (dapps), так и автономные блокчейны. Вот некоторые особенности, которые делают Avalanche уникальным:
- Скорость создания монет: максимальное предложение AVAX ограничено 720 миллионами токенов, но пользователи AVAX определяют, как быстро чеканятся новые монеты. Владельцы AVAX могут контролировать скорость создания новых монет, голосуя за корректировку суммы AVAX, которая выплачивается в качестве вознаграждения за добавление нового блока в блокчейн Avalanche.
- Структура комиссии за транзакцию: Стоимость обработки транзакции варьируется в зависимости от типа транзакции и загруженности сети Avalanche. Все сборы сжигаются — удаляются из обращения — чтобы со временем AVAX стал более дефицитным. Пользователи Avalanche голосуют за комиссию за транзакцию Avalanche, в результате чего комиссия AVAX может быть изменена.
- Механизм консенсуса: транзакции в блокчейне Avalanche подтверждаются с использованием уникального метода, который требует подтверждения транзакций множеством небольших случайных подмножеств участников сети, прежде чем транзакции будут считаться завершенными.
- Поощрения за участие: высокое время безотказной работы и быстрое время отклика могут увеличить количество вознаграждений AVAX, которые участник сети может заработать за обработку транзакций AVAX.
Avalanche обычно управляется механизмом proof-of-stake . Владельцы AVAX должны делать ставки — соглашаться не торговать или продавать — AVAX в обмен на право подтверждать транзакции AVAX. Владельцы AVAX с наибольшим количеством ставок и активно участвующие в качестве валидаторов с наибольшей вероятностью будут выбраны в качестве валидаторов для новых блоков Avalanche. Владение токенами AVAX также необходимо для голосования по предложениям по управлению Avalanche.
Преимущества и недостатки Avalanche
Давайте разберемся, что нравится и не нравится в Avalanche:
Плюсы:
* Быстрое время обработки транзакций
* Структура вознаграждения стимулирует участие
* Способен поддерживать множество проектов на основе блокчейна
Минусы:
* Жесткая конкуренция со стороны таких платформ, как Ethereum
* Валидаторы Avalanche должны поставить 2000 токенов AVAX.
* Злонамеренные или неосторожные валидаторы никогда не наказываются потерей AVAX.
Avalanche против Эфириума
Вам может быть интересно, чем Avalanche отличается от Ethereum. Avalanche заявляет о более быстром времени обработки транзакций — 4500 транзакций в секунду по сравнению с ограничением Ethereum в 15. Параллельный характер консенсусного протокола Avalanche — это то, что позволяет сети Avalanche проверять транзакции значительно быстрее, чем Ethereum.
В то время как Ethereum в настоящее время работает в гораздо большем масштабе, поддерживая гораздо больше проектов и транзакций, превосходная способность Avalanche к масштабированию может дать платформе Avalanche долгосрочное преимущество перед Ethereum. Avalanche может поддерживать большое количество транзакций, не требуя дополнительного времени для обработки этих транзакций.
Avalanche использует механизм консенсуса Proof-of-Stake, а Ethereum использует Proof-of-Work . Платформа Ethereum постепенно переходит на использование доказательства доли.
Avalanche и Ethereum также имеют разные структуры комиссий. Все сборы за обработку транзакций Avalanche сжигаются, в то время как сеть Ethereum сжигает только процент от комиссий за обработку транзакций. Комиссии на платформах Avalanche и Ethereum варьируются в зависимости от загруженности или загруженности сети. Структура комиссий для платформы Avalanche полностью контролируется пользователями.
Как я могу купить АВАКС (AVAX)?
Самый простой способ купить токены AVAX — через крупную криптовалютную биржу, такую как Coinbase или Kraken . Платформа Avalanche также поддерживает децентрализованную одноранговую торговлю между токенами AVAX и Ethereum.
Безопасен ли AVAX?
Avalanche можно считать безопасным из-за рандомизированного характера механизма консенсуса. Avalanche утверждает, что ее платформа поддерживает более строгие меры безопасности, которые делают блокчейн менее уязвимым, чем другие блокчейны, к атакам 51%.
Рискованно ли инвестировать в AVAX?
AVAX — это криптовалюта , которая считается рискованным активом. Вы можете инвестировать в AVAX, но сначала убедитесь, что понимаете риски и ограничения. Разумно не инвестировать больше, чем вы можете позволить себе потерять.